🧪 Types of Poisons
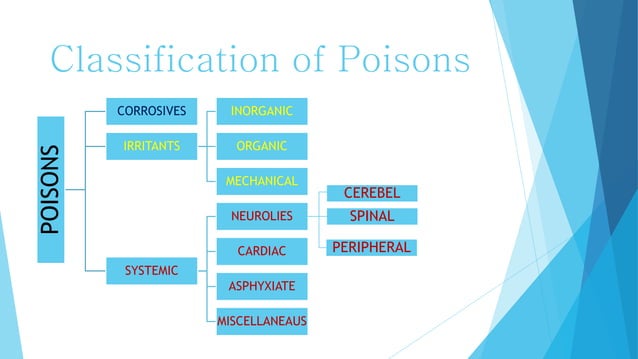
Poisons are classified into 6 main groups based on their Mode of Action.
(1) Corrosive Poisons
Corrosive poisons cause severe irritation, inflammation, and Ulcer formation in the Tissues. These poisons are essentially strong Acids or Alkaline.
They are further classified into the following subgroups:
I. Acids
| No. | Subgroup | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Mineral Acids | Sulfuric Acid, Nitric Acid, and Hydrochloric Acid. |
| 2. | Organic Acids | Oxalic Acid, Carbolic Acid, Acetic Acid, Salicylic Acid (Aspirin), etc. |
| 3. | Vegetable Acids | Hydrocyanic Acid. |
II. Alkalines (Bases)
| No. | Subgroup | Example |
|---|---|---|
| 4. | Alkalines | Caustic Soda, Caustic Potash, Sodium, Potassium, and Carbonates of Ammonium. |
(2) Irritants poisons
These poisons cause abdominal pain, cramps, vomiting, and diarrhea upon ingestion. Post-mortem signs are often prominent, such as redness or Ulcers found in the alimentary canal (gastrointestinal tract).
Irritant poisons are divided into the following categories:
No. Group Detailed Example (a) Inorganic Poisons This group includes both Metalic and Non-metallic poisons. * Metallic Poisons: Arsenic, Antimony, Mercury, Lead, Copper, Zinc, Bismuth, and radioactive elements.
* Non-metallic Chemicals: Phosphorus, Chlorine, Bromine, and Iodine.(b) Organic Poisons This group includes both Vegetative (Plant-based) and Animal poisons. * Vegetative Poisons: Abrus precatorius Croton tiglium , Nux vomica , Aconite, Red Chillies , Calotropis , Opium etc.
* Animal Poisons: Cantharides, Snake venom, Scorpion venom, and wood lice, etc.(c) Mechanical Poisons These poisons are classified based on their physical (mechanical) characteristics. Powdered glass (Kaanch ka Safuf), Chopped hair, and Diamond chips.
(3) Neurotic Poisons
- Most of these poisons affect the Central Nervous System (CNS), while some affect local nerves. Their use can commonly cause headache, drowsiness, dizziness, delirium, unconsciousness, coma, and sometimes convulsions or paralysis.
- Post-mortem signs are often not prominent. Therefore, the nature of the poison must be determined through the deceased’s History, symptoms and signs, and chemical analysis of the viscera (internal organs).
- The Neurotic Poisons are divided into the following subgroups based on the site of action:
No. Subgroup AffectedSite & Detail Examples (a) Cerebral Poisons Directly affect the Brain (Cerebrum). *Somniferous: Sleep-inducing poisons (e.g., Opium and its compounds).
* Inebriant: Intoxicating poisons (e.g., Alcohol, Narcotics, Sedatives, Turpentine oil, Petrol, and Agricultural chemicals, etc.).(b) Spinal Poisons Affect the Spinal Cord. Nux Vomica (Kutchla) and Yellow Jasmine.(Gelsemium sempervirens) (c) Peripheral Poisons Affect the Peripheral Nerves. Curare and Hemlock (Conium), etc.
(4) Cardiac Poisons
Poisons of this type disrupt the functions of the heart (cardiac activity)
- Examples: They often include vegetative poisons such as Digitalis (a type of squill), Oleander, Aconite, soapnuts and Nicotine.
(5) Asphyxiants Poisons
These are poisons that cause obstruction in respiration (breathing).
- Nature: These poisons are usually in the form of gas.
- Effect: They paralyze the lungs and the respiratory centers of the brain.
- Examples: Carbon Monoxide, Carbon Dioxide, gas from underground sewers, and certain war gases, etc.
(6) Miscellaneous Poisons
Certain drugs with a miscellaneous Mode of Action can produce toxic effects if used in excessive quantity.
They can be classified into the following groups:
- Analgesics and Antipyretics: Such as Paracetamol, Aspirin, and Analgin, etc
- Antihistamine
- Stimulants.
- Sedatives like Chlopromazine
- Hallucinogenic drugs
Routes of Poisons
Poison can enter the body through the following routes:
(A) Enteral Route:
This is the most common route. In this method, poison enters directly into the alimentary canal through the mouth or through the anus.
(B) Parenteral Route
In this method, poison is introduced into the body through injections by the following routes:
- Intradermal
- Subcutaneous
- Intra-muscular
- Intra-venous
- Intra-arterial
- Intraperitoneal
- Intrathecal
- Intrabonemarrow
(C) Inhalation Method
In this method, poison enters the body in the form of gas through respiration (breathing).
(D) Local Method
In this method, the poison is applied to a wound or to parts of the body where the skin has been destroyed.
(E) Through Physical Orifices
- Sometimes, poison is introduced into the body through natural orifices like the anus, vagina, urethra, nose, eye, or ear.
- It also enters the body through the mouth via the sublingual route. For example, a nitroglycerin tablet produces its effects in this manner.
